The realm of humanoid robotics stands on the cusp of significant transformation, as innovative collaborations push boundaries previously thought insurmountable. A recent partnership between 1X Technologies and Nvidia’s Gear Lab exemplifies this ambition. They are not just building robots for industrial applications but are also exploring their potential role within our homes. With the Neo Gamma humanoid robot as their flagship, the two companies project forward into a future where these machines may very well become household companions, helping us navigate daily tasks.
Founded in Norway and rebranded in California, 1X Technologies is no newcomer in the robotics field. While their focus has shifted towards more ambitious consumer applications since their establishment, the newly forged ties with tech giants like Nvidia signal their serious dedication to accelerate the development of general-purpose humanoid robots. “We’re super determined to bring general purpose humanoid robots into the world,” stated Eric Jang, the Vice President of AI at 1X Technologies, indicating a shared vision to unlock previously unattainable functionalities.
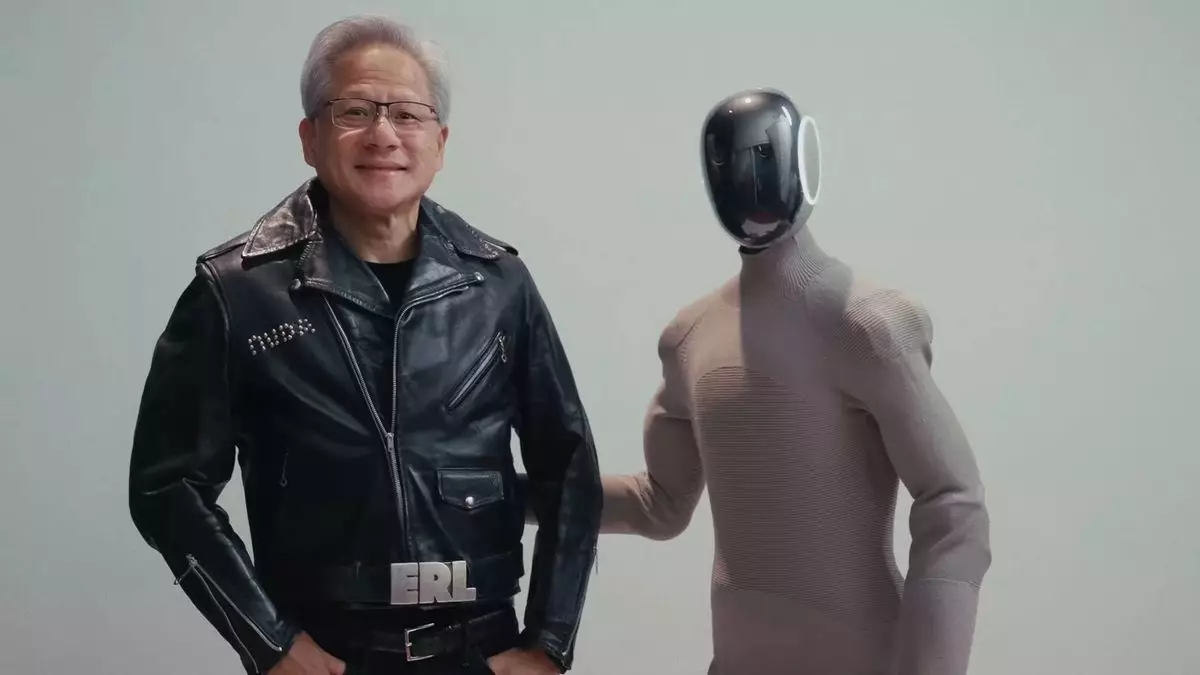
More Than Just a Fashion Statement
In an unusual marketing gimmick, Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang was presented with a custom studded leather jacket featuring the company’s logo, marking the collaboration’s announcement. While this spectacle might raise eyebrows in the tech world, it serves a higher purpose: to generate excitement and visibility surrounding advancements in robotics. The vivid imagery of a humanoid robot integrating into our physical and cultural landscapes isn’t merely whimsical; it’s a striking way to draw attention to the serious ambitions of this partnership.
Although one can appreciate the artistic flair of the jacket, the focus lies on the fundamental technical advancements that accompany this endeavor. Their autonomous capabilities are being showcased through tasks like loading the dishwasher—demonstrated in a recent publicity stunt as the Neo Gamma clumsily maneuvered its way through domestic chores. Watching the robot carry out these tasks with a certain level of hesitancy is illustrative of the ongoing learning process it is undergoing.
Creating the Framework for Learning
Behind the scenes, the collaboration involves sophisticated data collection and software development to enhance the Neo Gamma’s operational efficiency. 1X Technologies has created an API for accessing extensive datasets from both their offices and employee homes, complementing their efforts with a developer kit. The fluidity of actions—like grasping a cup and placing it into a dishwasher—is indicative of a complex feedback process where real-time data analytics play a critical role.
By setting a continuous 5Hz vision-action loop, the robot can act upon data it processes almost instantaneously. However, one must wonder: are we getting ahead of ourselves? While the tech sounds promising, the actual execution remains unproven in unstructured home environments, where countless variables can derail even the seemingly simplest tasks.
The Challenge of Real-World Deployment
What strikes me as particularly fascinating, yet troubling, is the disparity between the robot’s projected capabilities and the practical execution of those tasks. Promotional videos paint an approachable picture of drama and dexterity but often do not tell the whole story. For instance, the reality of the Neo Gamma hesitantly placing fragile items into dishwashers raises questions about how prepared such robots will be for delicate, everyday chores.
It’s crucial to consider that the development of humanoid robots is a complex journey, embedded with technical challenges that stretch far beyond simply teaching machines to mimic human movements. Indeed, as interesting as the robotic counterparts may be, they are still generations away from being seamless contributors to the household.
Hurdles Ahead: Are We Ready for Humanoid Helpers?
Despite the enthusiasm fueling these innovations, skepticism is warranted. With many thousands of hours of training data yet to absorb, the path toward practical household integration remains daunting. The concept of humanoid robots still feels like a distant dream rather than an imminent reality. As various projects in the field emerge—be it bartending robots or AI-powered companions—they bring both excitement and apprehension regarding our readiness to embrace them fully in our lives.
In the end, 1X Technologies and Nvidia may very well facilitate a critical advancement in the robotics domain. As we navigate a future increasingly populated by humanoid machines, we must remain grounded in the understanding that these technologies are still works in progress, balancing both potential and pitfalls along the way. The fascinating interplay between engineering ambition and practical application will ultimately determine whether they remain a novelty or become integral parts of our daily routines.